In today’s time, there is a great need to make the education system more interesting, in which learning and teaching can be improved by processing. As a result of which we can make teaching very useful. With the help of which the desire to learn in students and teaching skills in teachers can be developed. Due to all this, the entire teaching system will develop, which we are going to understand in more detail about learning and teaching through this article.

Learning is a comprehensive, continuous and life-long important process. Man starts learning after birth and keeps learning something or the other throughout his life. Gradually he tries to adjust himself to the environment. During this adjustment he tries to get the most benefit from his experiences.
Note: Almost all the topics of the B.Ed. programme have been described in detail on our website; this analysis is available to you in both Hindi and English, for which you can go to the menu and select the B.Ed. programme.
This process is called learning in psychology. The more power a person has to learn, the more his life develops. In the process of learning, a person performs many activities and sub-activities. Therefore, learning is an active response to a situation.
Learning is a continuous universal process. A person starts learning from birth and continues to learn something or the other till death. The pace of learning keeps increasing and decreasing according to the situation and need. There is no specific place for learning. One can learn anywhere, at any time, from anyone. Learning is also called learning. In the present study, learning and learning have been used as synonyms. Learning has the most important place in human life. Whatever behavior a person does or does not do, most of it is influenced by learning or the process of learning. In fact learning is the key to human life.
The process of learning can be influenced by many factors. Some of the major factors affecting learning are described further –
(1) Student related factors
- Willingness to learn
- Educational Qualification
- Aspiration level
- Intelligence
- Emotional state
(2) Factors related to teacher
- Knowledge of the subject
- Teacher’s behavior
- Teaching method
- Mental health and adjustment level of the teacher
- Desire to teach
(3) Factors related to subject matter
- Nature of subject matter
- Examples related to life
- Prior learning
- Difficulty level in different subjects
(4) Factors related to environment
- Physical environment
- Family environment
- Social and emotional environment
- Appropriate Content and Features
(5) Factors related to instruction
- Learning method
- Practice
- Knowledge of result
- Relating new knowledge to previous knowledge
Factors related to Learner
- Desire to Learn
If the child has a desire to learn then new knowledge can be taught to him in a simple way. If the child is not ready to learn then a very serious problem arises before the teacher. Desire, interest and motivation to learn influence learning to a great extent.
- Educational Achievement
The educational qualification of the student has a great impact on learning. If a student is backward in any subject then he will face difficulty in learning new knowledge related to that subject. If the educational qualification of the student in any subject is more than normal then the student would be able to learn new knowledge easily.
- Level of Aspiration
The success of learning depends a lot on the ambition of the child. Unless a student has ambition, he will not make efforts to learn.
- Intelligence
Learning depends a lot on the intellectual capacity of the learner. Children with fast growth learn faster than children with low intelligence.
- Emotional Condition
Emotional state is an important factor in learning. An emotionally healthy student learns quickly.
Factors related to Teacher
- Knowledge of the Subject
The teacher’s knowledge, experience and ability of a subject have a direct impact on learning. If teachers do not have knowledge of their subject then they will not be able to motivate students to learn.
- Behavior of the Teacher
Teacher has an important role in the learning process. The conduct, thoughts and behavior of the teacher have a great influence on the children and they also try to imitate them.
- Method of Teaching
Teaching method is directly related to the learning process. Not all children can learn in the same way. The more effective and scientific the method of teaching is, the more beneficial it will be for learning. Learning by doing, learning by observation, learning by experiment, game method etc. have their own importance.
- Level of Adjustment and Mental Health of the Teacher
Those teachers who are mentally disturbed and unwell. Or those who are unable to adjust themselves as teachers, they always lose their balance in the field of teaching and there is no limit to the amount of harm they can cause to children. On the contrary, well adjusted and mentally healthy teachers prove to be a boon for teaching and students.
- Will to Teach
Only those teachers who have the desire to teach are able to teach children successfully. People with no desire do not make various efforts to teach. They cannot arouse interest and curiosity in learning among the students.
Factors related to Subject-Matter
- Nature of Subject-Matter
The nature of the subject matter also affects the learning process. Simple and interesting subject matter is learned more quickly than difficult, boring and uninteresting subject matter.
- Examples Related to Life
If there are examples in the subject matter which are related to the child’s life and the child is well acquainted with them, then it is easier to remember them and they are remembered for a longer time.
- Previous Learning
How quickly or how well the child learns a subject matter. It depends on what he has learned before. The process of new learning does not start from scratch but starts from the knowledge previously acquired by the child.
- Difficulty level of Different Subject
Difficulty level varies in different subjects. A student learns very well in one subject whereas in another subject his learning may be very slow.
Factor related to Environment
- Physical Environment
It is necessary to have a conducive environment for learning. In adverse circumstances the learning process cannot be completed properly. Appropriate physical environment for studying, such as clean air and light, cleanliness and seating arrangements, etc. also affects learning.
- Family Environment
The family plays an important role in a child’s learning. In families where there is a peaceful and harmonious environment, children are able to learn quickly. A discordant environment hinders learning.
- The Socio-emotional Environment
The kind of social-emotional environment that is available in the classroom, school and other learning situations to carry out the teaching-learning work properly, the better the learning process will be conducted.
- Appropriate Learning Material and Facilities
When children get suitable study material and facilities, they achieve promising success. On the contrary, students who do not get the necessary equipment, more materials and facilities to help in learning (textbooks, other materials for reading and writing, library, laboratory facilities, necessary time and facilities for doing homework, etc.), they Fall behind.
Factors related to Instruction
- Learning Method
The learning method adopted by the teacher affects the learning of the student. Not all children are affected by one method of teaching a subject. If a teacher teaches his subject under pressure in an unscientific and non-scientific way, then the children do not take interest in it. But teachers who choose the learning method according to the interest, ability and need of the children, children remain enthusiastic in their class.
- Practice
Practice has a great influence on the process of learning. Doing a task repeatedly increases the speed of work and reduces errors. Pride learned through practice is permanent.
- Knowledge of Achievement
During learning, if the progress of learning is known from time to time, then the learner remains enthusiastic. He becomes aware of his errors and hence he corrects them. Knowledge of the outcome of learning serves as reinforcement.
- Relating new knowledge to previous knowledge
When new knowledge is taught by relating it to previous knowledge, the child learns quickly.
It is often seen that after an animal learns a task, it becomes very easy and convenient for it to learn or do other similar tasks. In fact, when a person tries to do or learn a new work, the knowledge or experiences he has acquired earlier play an important role in doing or learning that work. In fact, while doing or learning work in other situations, there is definitely some transfer of previous experiences or knowledge. Learning of one subject affects the learning of another subject.
According to Atkinson (Atkinson, 1998)
“Learning transfer refers to the effect of prior learning on current learning, if it helps in learning the new subject then it is positive transfer, if it hinders the learning of the new subject then it is negative transfer.”
There are three types of transfers-
1- Positive Transfer
When past learning helps in present learning, it is called positive transfer. In other words, when learning of one situation or topic helps in the absorption of another situation or topic, it is called positive transfer. For example, after learning Hindi, it becomes easier to learn Bengali.
2- Negative Transfer
When learning of one situation or subject hinders the learning of another situation or subject, it is called negative transfer. For example, after learning one list of meaningless words, it becomes more difficult to remember another list. Here the first habit hinders the formation of the second habit.
- Zero Transfer
When learning of one subject or situation neither helps nor hinders the learning of another subject or situation, it is called zero transfer. Here the earlier teaching does not affect the present teaching in any way. For example, the effect of throwing a ball or learning to swim is neither helpful nor hindrance in learning English or Hindi.
Students need to learn inside and outside of school
The aim of the school is to prepare students for life beyond school. In today’s society there is greater demand for self-awareness and more specialized skills. The easiest way to help students grow is to incorporate learning experiences outside the classroom. Taking classroom learning outside can help enrich a student’s educational experience by showing them real-life applications of the principles they are learning in school.
Classroom learning is a traditional method of learning in which the learning environment is created within the physical walls of the classroom. As the name suggests, classroom learning requires both the teacher and the student to be physically present inside the classroom.
Example: From the time a student enters education, the entire educational system is based on the method of learning in the classroom. From nurseries, schools to senior schools, colleges and universities – most of these are based in the traditional learning space, which is the classroom.
- Compliance with certain rules and principles
- Compliance with instructions
- Fixed curriculum and curriculum
- Development of intellectual and logical abilities
- Based on reliable
What is learning outside the classroom?
Learning outside the classroom is the use of places other than school for teaching and learning. It’s about getting children and young people outside, providing them with challenging, exciting and different experiences to help them learn.
Space may refer to a place, activity, or workshop, but regardless of where learning occurs outside the classroom, the objective is the same. Give students real-world learning experiences that will prepare them for success in life beyond school.
Learning experiences outside the classroom differ from those produced through traditional teaching methods because students can be encouraged to incorporate a broader range of skills such as teamwork, leadership, and compromise into their learning environment.
Traditional teaching focuses on repetition and memorization to educate students and is beneficial for sharing new knowledge and teaching students who learn best by listening. However, traditional teaching does not encourage students to develop the critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making skills that learning outside the classroom can do. Learning outside the classroom can not only lead to a deeper understanding of challenging concepts, but it can also provide a context for learning in many areas.
Benefits of learning outside school
- Encourage learning by doing
- Development of practicality
- Development of sociality
- Fulfillment of need
- Development of human values
Role of teacher in teaching-learning
1- Role as a giver of knowledge
The role of the teacher is as a giver of knowledge. The teaching-learning process should be taught to the teacher in such a way that the students are educated. Stock exchange should play a role in the books of students and books of students with the help of books. Teachers play an important role in developing insight in children. That is true knowledge. When students self-generate knowledge.
2- Role as Facilitator
Teachers have to create such a good learning environment for the students that makes them comfortable in education. The role of the teacher is that of a source of knowledge as well as a facilitator. It helps in the process of converting information from various platforms into knowledge and understanding. He helps the students appropriately.
3- Role as a guide
Teachers and students are guided in various ways. He gives guidance related to career etc. to the students on the basis of their actual qualities. He judges and guides the students on their support, courage, ability, academic ability, scientific etc.
The teacher acts as a disseminator of knowledge, facilitating information and knowledge creation. It develops teaching-learning in a free environment. He gives knowledge and guidance to the students in their development without any discrimination on the basis of caste, religion, region, community and class. He prepares the students in such a way that they get coordination among different sources of knowledge.
4- To develop emotion of the learner
The teacher develops emotional development in the students through the process of education. This development is easily accomplished by the teacher’s sympathy, love, proper work, personal contact and proper guidance.
5- Teacher as Source Information
The teacher provides new information of knowledge to the students through teaching. He makes them aware of different types of ideas and things. Teachers who know the method of subject presentation get considerable success in this field.
To make the teaching-learning process effective and efficient, it is necessary that the teacher helps in increasing the knowledge of the students. Teacher has the following roles in teaching learning-
- He should be an informant.
- He should be the one providing the resources.
- He should work as a craftsman and artist.
- The teacher should be working as a manager.
- He should act as a guide.
- The teacher should act as a philosopher and friend.
- It should act as a major source of knowledge for the community.
- The teacher should act as a protector of the self-respect of the students.
- The teacher should act as a confidant of the students.
- He should work as a consultant and innovator.
- He should act as a guardian.
- He should act as an upholder of moral values.
Cognitive Development Theory of Piaget
Jean Piaget (1896-1980) did not give any concept of psychology and did not undertake any study, yet his name is leading among the scholars of psychological research of children. He was a zoologist from Switzerland. At the age of 22 he obtained his doctorate in zoology on Mullusks of Vlios. In 1920, he joined the Vinet Testing Laboratory in Paris. While observing, dissecting and experimenting with children, he propounded his educational theory regarding cognitive development or child perception. Piaget started his study of art development by observing his own three children. In the course of this beginning, he further explored other children.
According to Piaget, the cognitive development of children takes a new direction from adolescence. Piaget suggested that a special stage of cognitive development begins from adolescence, which is called the stage of formal operations. In solving a problem, the child in this stage examines all aspects of that problem, collects all possible solutions in the mind and also examines the relationship between all the properties of an object. In solving a problem, the child does systematic deductive thinking, which is clearly this type of scientific thinking because it contains all the possible solutions to the problem and the child reaches a final scientific conclusion by logically sorting out all the inappropriate solutions. The quality of formal operations among adolescents is influenced to a large extent by their educational level. The gradual development of psychological concepts made by him is called the theory of cognitive development.
piaget’s stages of cognitive development
Piaget traces the beginnings of human cognitive development to biologically underlying ways of interacting with the environment. He has divided the stages of cognitive development of the child into the following 4 categories-
(1) Sensory Motor Period
(2) Pre-operational Period
(3) Concrete operational period
(4) Formal operational period
(1) Sensory Motor Period
This is the stage from birth to 2 years. In this, children get primary experience through their senses. According to Piaget, the cognitive development of the child in this stage takes place in the following 6 stages-
(i) stage of instinctive actions
This stage lasts from birth to 3 days. In this state, the child does only spontaneous actions. In these activities, children do the most sucking action by taking any object in their mouth.
(ii) stage of elementary circular reactions
This stage lasts from 1 month to 4 months. In this stage, the instinctive actions of children are modified to some extent by their experiences, repeated and coordinated with each other. These responses are called primary because they are the main responses of the child’s body and they are called circular because the child repeats them again and again.
(iii) stage of secondary circular reactions
This stage lasts from 4 months to 6 months. In this stage, children respond by touching objects and moving them around. They also do some such reactions, which give them pleasure.
(iv) State of coordination of secondary schemata
This stage is from 8 months to 11 months. In this stage, children start to differentiate between the goal and the means to achieve it and start imitating the actions of their elders. In this stage, children begin to generalize the schemas they learn.
(v) State of field responses
This stage is from 11 months to 18 months. In this stage, children learn the properties of objects by trial and error.
(vi) Stage of discovery of new resources by human coincidence
This stage is from 18 months to 24 months. In this stage, the child begins to understand the existence of the object seen even in its absence.
(2) Pre-operational Period
This is the stage from 2 years to 7 years. According to Piaget, the cognitive development of the child in this stage takes place in the following 2 stages-
(i) Pre-functional functional state
This stage is from 2 years to 4 years. In this stage, children begin to establish relationships between objects and words in the objects and creatures around them. They learn all this often through imitation and play.
(ii) Insightful functional state
This stage is from 4 years to 7 years. In this stage, children start learning language and start thinking and reasoning, but there is no orderliness in their thinking and reasoning. In this stage, children learn to express in their own way what they have learned from the point of view of language. In this state, images of objects also start forming in their brain, that is, their imagination starts working.
(3) Concrete operational period
This is the stage from 7 years to 11 years. This stage is the stage of knowledge of tangible actions. Children start understanding these and the facts related to them. In this stage, children also begin to understand that even though the shape or form of an object may change, there is no reduction in its weight etc. Similarly, there is no change in the volume, number, amount, weight, quantity etc. of the object.
In this stage, children are more practical and realistic. They develop the ability to reason and solve problems. They start looking for solutions to concrete problems but cannot think about abstract problems.
(4) Formal operational period
This is the stage from the age of 11 to adulthood. In this stage, systematicity starts coming in the thinking of the children. They start doing rational activities. They start thinking, intellectual activities and problem solving at an emotional and abstract level. Now they have the ability to prove the validity of any logical argument on a formal level even after moving away from its opposite thematic context. According to Piaget, in this stage, children also understand the meaning of symbolic words, metaphors and similes and start flying high in the formation of abstract concepts.
Constructivism is made up of two words Rachna + Vaad, Rachna means creation, Vaad means idea, that is, it literally means creating ideas. This is the natural or natural principle of learning. In this, ideas are formed on one’s own by collecting information from different sources which is reflected in the conduct of individuals. In constructivism, knowledge is created in students through their own experiences by interacting with the environment. In constructivism the role of the teacher is that of a facilitator, which includes providing opportunities for the development of abilities and comprehensive assessment.
The root word of constructivism is “construction”. Basically, the principle of constructivism is that knowledge must be created by a person, not simply transmitted by a person. People brought new information and combined it with their pre-existing knowledge to create knowledge. It takes time to make the effort to learn the study of constructivism.
Importance of constructivism in the process of learning
1- Student Centered Learning
Constructivism is actually student-centered learning in which priority is given to how students can develop cognitively through social interaction.
2- Development of creativity
Creativity actually develops in students through constructivism, through which many types of creativity can be seen. Because in constructivism, students get that opportunity to develop their creativity to the extent possible.
3- Development of practical approach
Through constructivism, practicality is developed in the students in which the person adjusts the information collected from the society in the practical context.
4- Learning through experience
Whenever we get a new experience, we process it in our mind. We will use that experience to understand our world.
5- Cognitive imbalance
When we are exposed to a new experience, it may be contrary to our prior knowledge. A learner will become confused and not understand what he or she can see. At this point, a learner is in a state of cognitive dissonance. We always want to be in a state of cognitive balance where everything makes sense.
1- Activating prior knowledge
2- Acquiring new knowledge
3- Understanding new knowledge:
4- Using new knowledge
5- Reflecting new knowledge
Main features of constructivism
1- In creative approach, students work in groups and the student himself creates knowledge.
2- In the creative approach, the classroom environment is democratic.
3- In this approach more and more teaching learning material is used.
4- The teacher helps in the learning process due to which students remain enthusiastic to work as a responsible member.
5- Constructivist approach focuses not on teaching but on learning.
6- In this approach students are encouraged to ask questions.
The English word ‘Motivation’ originates from the Latin word ‘Motum’, which means move motor and motion. In the psychological sense, by motivation we mean only the internal stimuli on which our behavior is based. In this sense, no importance is given to external stimuli. In other words, motivation is an internal force, which can motivate a person to do work. It is an invisible power, which cannot be seen. This can only be estimated by observing behavior based on this.
There are two types of inspiration-
(1) Internal motivation
(2) External motivation.
1- Intrinsic Motivation
Under this motivation, the child does any work on his own will. By doing this work he gets happiness and satisfaction. The teacher provides positive inspiration to the child by organizing various types of programs and creating situations. This motivation is called intrinsic motivation.
2- Extrinsic Motivation
In this motivation, the child does not do any work due to his own will, but due to someone else’s wish or external influence. By doing this work he achieves some desirable or definite goal. The teacher motivates the child by using praise, criticism, rewards, competition etc. This motivation is called extrinsic motivation.
There are four major sources of inspiration:
(1) Requirements
(2) Drives
(3) encouragement
(4) Objective.
(1) Requirements
Every person who exists in this world has to make efforts to satisfy his needs or wants. In the words of Boring, Langfeld, and Veldt, “A need is a tension within the organism which organizes the field of the organism in relation to certain incentives or goals and stimulates activity directed toward their attainment.”
Needs are relatively permanent tendencies that seek their satisfaction in achieving some specific goals. When these goals are achieved, it is no longer needed for some time. A need is different from a want in the sense that I want a car. It may be a want or desire but not necessarily a need. But there is always a need.
(2) Drivers
The needs of living beings give rise to their respective drivers. For example, food is a need of living beings. This need gives rise to hunger-drive in him. Similarly, the need for water causes thirst. A driver motivates an organism to perform a certain type of action or behavior, for example, a hunger driver motivates it to eat food.
(3) encouragement
Those environmental objects which satisfy the desires of a living organism are called stimuli. For example, the motivation of hunger is satisfied by food, so food is called a stimulus. But needs are driven by internal needs whereas stimulus is a thing or being that is found in the environment. Incentives excite, excite, and move toward action when they are associated with certain stimuli that signal their presence.
(4) Objective
Motives take a variety of forms and are specified by many different terms such as needs, desires, stresses, sets, determining tendencies, attitudes, interests, persistent stimuli, etc. Some psychologists call motives innate or acquired energy, and some psychologists call them physical or psychological states.
In an organization, if employees are motivated, they will show greater commitment towards the achievement of organizational goals and objectives.
1- Productive use of human resources
2- Less absenteeism and turnover
3- Good corporate image
4- Development of friendly relations
5- Achievement of goals
1- Productive use of human resources
Human resources are valuable assets of an organization. Poor performance of employees can have a serious impact on the performance of the organization. If employees are motivated, they will make efficient use of their skills and competencies to perform tasks, thereby increasing overall organizational efficiency.
2- Less absenteeism and turnover
Motivated employees are less likely to be absent or leave for other organizations. High rates of absenteeism and attrition can bring financial losses to an organization, which adversely affects its performance. Motivated employees do their work with more zeal and enthusiasm, do not take leave frequently and show stability in the organization. Furthermore, motivated employees are loyal to the organization.
3- Good corporate image
Employees play an important role in influencing the corporate image of an organization. If employees are motivated to work efficiently, they will also work towards meeting the needs of customers. This creates a good image of the organization in the market.
4- Development of friendly relations
Motivated employees are usually open to expressing their ideas with others. It bridges communication gaps and resolves disputes between employees; Due to which cordial relations will develop among the employees and between the management and the employees.
5- Achievement of goals
Motivation drives goal-directed behavior that encourages employees to exert their efforts.
Role of motivation in teaching-learning process
(1) Motivations direct behavior
That is, they give a kind of direction to a person’s behavior due to which he gets a satisfactory feeling. The teacher should make his pupils active and motivated to put their energies on well-defined and attainable goals.
(2) Objectives energize behavior
That is, they provide energy to the learner in his learning activities. Rewards motivate further success and punishment for failure motivates action for achievement. Therefore objectives like rewards and punishments etc. are very helpful in the learning process.
(3) Selecting objectives
That is, we select only those learning tasks that are supported by our objectives. They prompt the learner to react to certain situations and ignore others i.e., they help the learner to elicit correct responses and eliminate incorrect responses.
(4) Helpful in attracting attention
Inspiration helps capture attention. Teachers can help students concentrate on their studies by motivating them.
(5) Helpful in developing interest
Motivation is an art of creating interest among students. Therefore, by motivating the students, the teacher can arouse interest in their work.
(6) Knowledge acquisition
Motivation helps in quick acquisition of knowledge. Therefore the teacher can motivate the students to acquire more and more knowledge by using the best methods of teaching.
(7) Helpful in character building
A teacher can inspire students to achieve the best values and ideals. Thus, he can help in building their character.
(8) Development of social qualities
Motivation helps in the development of social qualities. The teacher can motivate students to develop a sense of community and social qualities by encouraging them to participate in group activities.
(9) Development of sense of discipline
The teacher can motivate students for desirable activities. He can solve the problem of indiscipline by developing a sense of discipline among the students.
(10) Progress according to individual differences
The teacher can help students to work according to individual differences by using appropriate motivation. Thus, it can provide opportunities for students to make progress in line with individual differences.
(11) Cornerstone of personality
Motivation plays an important role in the physical, intellectual, emotional, social, educational, professional etc. development of personality. It is considered the cornerstone of personality. The teacher should motivate the students from time to time with the aim of helping them in the best development of their personality.
Teaching is a social process. The word teaching is derived from the English word Teaching, which means to teach. Teaching is a three-dimensional process, in which teachers and students acquire their form through the curriculum. That is, the exchange of ideas or mutual interaction between the teacher and the learner using any subject matter as a medium is what we call teaching.
The narrow meaning of teaching is related to school education in which the behavior of a child is changed according to the curriculum by the teacher at a specific place and in a specific environment with certain teachers. In this, the teacher gives some knowledge or advice to the student in the class.
The broad meaning of education includes everything that a person learns throughout his life. That is, the broad meaning of education is that in which a person learns through formal, informal and non-formal means. In this, the learner keeps developing all his powers progressively from birth till death.
The nature of teaching can be explained in the form of the following statements-
(1). teaching is an internal process
It is conducted for special work between teacher and students. In this, the process of teaching takes place in the classroom in which both the teacher and the learner are involved. If the teacher continues to give a blank lecture and the learner remains a passive listener, then interaction will not be possible.
(2). Teaching is both an art and a science
The nature of teaching is both artistic and scientific. The nature of teaching planning and evaluation activities is more scientific whereas the process aspect of teaching is artistic in which the teacher uses his skills. The presentational aspect of teaching is the art in which appropriate teaching skills are used by the teacher in such a way that the learners understand the subject matter well and other learning objectives are achieved. To ensure that teaching does not become monotonous, an element of entertainment is also given.
(3). learning is a developmental process
Through the process of education, children are developed and desired changes in their behavior are brought about. Cognitive, emotional and functional aspects are developed.
(4). learning is a continuous process
Teaching is a continuous process which continues till the teaching-learning objectives are achieved. It has three aspects – action, teaching and evaluation.
(5) Teaching is a process of direction
In teaching, efforts are made to develop the students according to their abilities. In this way the aim is to direct.
(6). Teaching is a tripartite process
Most of the educationists have called teaching as a tripolar process. According to Bloom, there are three aspects of teaching – (i) learning objectives, (ii) learning experiences and (iii) behavior change.
(7). Teaching is a purposeful process
Teaching activities are done to achieve some specific objectives. For them it takes the form of a similarly planned process.
(8). Teaching is a social and professional process
The process of teaching is carried out in a group of teachers and students. It is absolutely necessary to have at least one teacher and one student. Teaching is a professional activity which people use as a means of earning their livelihood and are called teachers.
(9). learning is measured
Teaching is measured in terms of teacher’s behavior. Teacher behaviors are also measured and behavior patterns are analyzed through observation methods.
(10). teaching is a science
The skill aspect of teaching presentation is an art, but their actions can also be logically observed and evaluated. This provides scientific basis to it.
(11). Teaching is a formal and informal process
The education process is carried out in the school according to a fixed program and is also conducted outside the school.
To fulfill his teaching responsibilities, a teacher has to carry out various types of teaching activities with his students and for this he has to go through proper procedures related to systematic planning and implementation. To do all this, he has to move forward by organizing his teaching work in certain steps or stages.
These steps or stages are called teaching stages or teaching phases.
According to Jackson, the teaching process can be divided scientifically into the following three stages.
There are many activities related to teaching which the teacher has to do before classroom teaching. In these activities, the teacher sets the objectives of classroom teaching according to his ability and experience. Makes a plan as to which course material should be presented in which order to achieve the objectives. According to this plan, he selects teaching methods and makes a specific strategy for teaching. All these activities are very important to make the lesson successful. The success of other steps of the teacher is based on this step only.
The teacher prepares the lesson himself and the help of a subject expert person can be taken. Textbooks and supporting/reference texts can become the basis for preparation. Preparing a plan for teaching is an important task in this stage. This can be in written or oral form (mentally preparing for study). In this, the teacher prepares to achieve the desired objectives before entering the class. The teacher takes decisions related to content and method.
The following verbs are included in the pre-verb state
(i) Determining the objectives of teaching
The teacher decides the objectives before teaching in the stages of teaching. After determining the objectives, he also clarifies them in the form of behavioral change. In this the teacher also decides what will be the objectives in the form of pre-behavior and final behaviour.
(ii) Selection of course material
After determining the objectives of teaching, the teacher will select the subject matter. The teacher will see why this content is necessary for this course and what level of motivation will be effective for the students and what methods should be used for their evaluation? Etcetera.
(iii) Sequencing of parts of the text
After the teacher has selected the objectives and the subject matter, it is very important to keep the various parts of the subject matter in a systematic manner. This sequence of curriculum should be maintained in a psychological manner so that the child can learn well.
(iv) Teaching array
Decision regarding composition: In this process, the teacher thinks about which teaching strategies he should use to impart knowledge to the students on the basis of age, maturity, abilities etc. so that the students can easily acquire the knowledge. Can do. All the training institutes provide knowledge about various strategies to the student teachers so that they can select the right strategies in the class and can do the teaching work smoothly.
(v) Selection of teaching strategies
Even before going to the class, the teacher should decide which teaching tips and techniques, examples and supporting materials he will use while teaching to clarify which teaching points of the subject matter. When will he ask questions in the class, give lecture and at what time which audio-visual material will he use? The teacher should plan in advance how and through which techniques he will evaluate the teaching.
This stage or stage includes all the teaching activities that the teacher does after entering the classroom. All activities related to presentation of text are included in it. The teacher has to use different types of skills in the classroom. Out of these, classroom management skills and communication skills are very important. The teacher’s skill in classroom arrangement is very important in his teaching work. While going to class in school, the first thing one has to do is to use the skill of classroom arrangement. Good teaching depends a lot on the skills of classroom arrangement. It is only through this skill that a suitable environment for learning is created. Therefore, proper seating arrangement of students in the class, necessary equipment and arrangements of the class (furniture, carpet, blackboard, chalk, duster) etc. have to be kept in mind. Arrangements should be made for the students to sit in the class according to their height, keeping in mind visual impairment, hearing impairment etc. The classroom should be arranged according to educational activities, physical and social activities. After the preparation stage, the second stage is to move to the actual stage of teaching.
The following activities mainly take place at the interaction stage of teaching.
- Perception of class size,
- Diagnosis of students,
- Action and reaction. This includes the following things
(a) Selection of stimulus,
(b) presentation of stimuli,
(c) use of tactics,
(d) Extension of tips.
(i) Classroom experience
In the process of teaching, first of all the teacher goes to the class and this process starts from here. In this the teacher gets a feel of the size of the class. After this he feels about the students. At the same time, students also feel about the teacher. In relation to the students, the teacher finds out which students are motivating and which are frustrating? Which students are problematic and which students are helpful in studying; With this the teacher gets to know the exact status of the students. Along with this, students also get to experience the personality of the teacher within a short time.
(ii) Students’ level of knowledge
The second main step in the teaching process is to obtain knowledge of the students’ level. It is very important for the teacher to know how much knowledge he has about his subject and what is the level of general knowledge. For this he takes the help of various questions. The knowledge and level of the students can be easily known through questions.
(iii) Response and Feedback Teacher
All the actions and reactions that go on between the learners are included in it. It includes both verbal and non-verbal actions and reactions. Learners respond to what the teacher says or does, and the teacher responds to what the learners say or do. This action-reaction has special importance in teaching.
(a) Selection of stimulus
Motivation has great importance in the action-reaction between teacher and student. Therefore, the teacher has to decide which motivator is effective during teaching and which is not? Only through this inspiration can the desired conditions of teaching be created. While presenting the stimuli, the teacher must keep in mind the sequence of teaching.
(b) presentation of stimuli
The teacher will also have to see in what context and in what form these motivational words are to be presented? They will be more useful if presented in the same context and format.
(c) Back-nutrition and reinforcement
To increase response, it is very important to do feed-back and reinforcement in teaching. These help in teaching. It is of two types, positive and negative.
In ‘positive’ reinforcement the teacher motivates the students. By praising, praising, giving awards, etc. This greatly increases the possibility of expected and desirable actions taking place. Negative reinforcement includes scolding, punishing, humiliating, etc. Due to this, there is no possibility of undesirable actions happening again. The purpose of both positive and negative reinforcement is to improve the behavior of students.
(d) expansion of teaching, strategies
Reinforcement strategies control the verbal and non-verbal behavior of students and are helpful in presenting the content effectively. Expansion of methods of education helps in making the interaction between student and teacher effective. The following facts are kept in mind while developing teaching strategies.
The last step of the teaching process is related to teaching or evaluation of students. Without evaluation, teaching remains incomplete. Under this stage, the teacher evaluates the knowledge given through various formal and informal methods and checks in which direction and to what extent the desired behavioral change of the students has taken place. Teaching is conducted to achieve some educational objective. Through evaluation, the teacher finds out how successful the teaching was in relation to the objectives, that is, to what extent the students could achieve the educational objectives. In this stage of teaching, the teacher measures and evaluates the desired behavioral changes in students with the help of oral or written or practical tests. The main activities of this step are as follows-
- Measurement of desired behavior of students by the teacher.
- Selection of appropriate evaluation techniques.
- Consideration of improvement and development of instructional and teaching strategies and changes in teaching strategy based on students’ results (achievement of objectives).
Difference Between Teaching and Learning
| Teaching | Learning |
| 1. Teaching is an action that changes the behavior of children.
2. Teaching is given to fulfill pre-determined objectives. 3. Teaching is the reason. 4. There are other activities of teaching – like speech, question-answer process, motivating, giving direction etc. 5. Teaching is related to the teacher. 6. Teaching happens as per the wish of the teacher. 7. Teaching is a social work. 8. The teacher who teaches gets a salary. 9. Teaching work can be evaluated as success or failure. 10. The teacher comes to the class after reading the subject matter before teaching. 11. The process of teaching changes the nature of both the teacher and the students. 12. Every teaching definitely has some definite objective. 13. Teaching is mostly formal. |
1. Learning is a process which impacts the personality of children.
2. The goal is achieved through learning. 3. Learning is work, there is result. 4. Listening in learning, giving answers after listening, giving direction and encouragement by the teacher etc. 5. Learning is related to the student. 6. Learning happens as per the wishes of the children. 7. Learning is an individual task. 8. But children have to pay fees to learn. 9. Children definitely acquire something while learning. 10. Learning is beneficial for children. 11. Children come to class without reading the subject matter. 12. The process of learning changes only the nature of the students. 13. Learning can be formal and informal. |
1- The scope of learning is wide whereas the scope of teaching is not so wide.
2- Teaching is not the only means of learning. Apart from education, the animal also learns through its experience, senses, imitation and intuition etc.
3- Teaching affects only a part of a person’s personality, whereas learning affects the entire personality.
4- Teaching is always formal. Whereas learning is of both formal and informal types.
5- Teaching is a work system and learning is its result.
6- Teaching is a social task whereas learning is an individual task. Teaching is a complementary process whereas learning is a performance oriented process.
Relationship between Teaching and Learning
There is a close relationship between teaching and learning. Although it is not necessary that there should be learning in every teaching, but it is certain that the basic and only ultimate objective of every teaching is learning. If we look at it from the objective point of view, we can say that teaching is the means and learning is the end. Teaching is a process and learning is its result. Thus teaching and learning are related to each other. The teacher organizes his teaching based on the prior learning of the students in the class. The level of teaching will have to be according to the situation and condition of the students’ previous experiences. Not only this, the teacher will have to use teaching techniques and policies accordingly. Teaching principles are developed on the basis of learning principles. In fact, teaching is the organization of learning situations. The basis of teaching and learning is educational psychology. Both teaching and learning formulate their respective principles on the basis of the principles of psychology.
- Learning is impossible without teaching
Learning is not possible without teaching. The feeling is that unless there is someone to educate or teach, what will the student learn from whom. His learning will remain incomplete.
- Learning goal of teaching
Learning – Without learning, teaching has no importance. The reason is that teaching happens only for learning, rather we can say that the aim of teaching is learning. Therefore, if there is no learning, there is no teaching.
- Teaching and learning arts
Teaching and learning both are noble arts. If teaching is an art then teaching is also an art. Hence there is a deep connection between the two. Both are dependent on each other.
- Related to teaching and learning time
Both teaching and learning are related to time. This means that according to the type of country and time, the same type of teaching and learning will take place. During the times of dictatorial kings, teachers used to teach children in a dictatorial manner. Children were not independent, but in a democratic government system the teacher teaches in a democratic manner. This is the reason why teachers who teach in a dictatorial manner cannot be called successful teachers.
- Commonality of goals
There is also similarity of goals in teaching and learning. The aim of teaching is learning and learning is the achievement of the aim of teaching.
- Based on rules
The biggest similarity between teaching and learning is that both are based on certain rules. If the teacher follows these rules properly then the objectives of both teaching and learning are achieved.
Principles of Effective Teaching
The teacher tries to bring change in the behavior of the student through teaching. Teaching is an art and teacher is an artist. Every art has some principles. Those become the principles of the teacher or artist. Similarly, there are principles of teaching also. With the help of these principles the objectives of teaching can be achieved.
The principle is to organize any subject, field or process in a scientific manner so that that process can be clearly visible to everyone.
(1). Principle of Motivation
It is human nature to be happy with praise and disappointed with criticism. After receiving praise, we decide to perform better or work harder and are also successful in it. This praise and praise is called inspiration in the language of psychology. Inspiration makes a living being active. Every action of a person which wants to achieve some goal is motivational.
In fact, motivation is the process that starts all types of learning and continues until its completion. The teacher should make learning interesting through motivational elements so that effective communication is possible. Once motivated, the learning process becomes faster and therein lies the success of teaching. In the present teaching method, great importance has been given to motivation. Without motivation a child cannot take interest in any work. Successful teaching is that in which children get maximum inspiration from the teacher to do their own work.
(2). Principle of Activity
It means learning by doing. This theory is the basic principle of child psychology. In this, it is extremely important for the learner to remain active throughout the learning process. In modern teaching method, the principle of learning by doing is being completely followed. A child cannot develop by listening to speeches and memorizing books. This can be done through the same teaching method which encourages the child to do more and more physical and mental work. This is called successful teaching method. In this, children are given maximum opportunity to reason and think and fight problems.
In the process of learning cycling, we cannot learn to ride a bicycle unless we do activities like holding the bicycle, pedaling, falling many times while riding, etc.
(3). Principle of Interest
We easily learn the subject or activity in which we are interested. Because we do it with great urgency. Therefore, some skilled teachers pay special attention to the interests of children while determining teaching methods. For this, while selecting special teaching materials, he closely observes the child’s wishes, needs and the circumstances prevailing around him. According to the principle of interest, the teaching work should be such that the learner learns it with full concentration. Teachers should present the teaching material in such a way that class discipline is maintained and learners remain active in learning.
(4). Principle of Definite Aim
No creature works unnecessarily. Every work of his has some definite purpose. The more faith and devotion he has in his heart towards that objective, the more effort he puts in to achieve it. A person does any work to fulfill his selfishness. Therefore, the worker gets sufficient inspiration from the purpose of the work. Another direct benefit of having a definite objective is that the work done by children can be sequenced. Any work is done to achieve some objective and that work continues till the achievement of that objective. Similarly, in the class too, the children are first told the objective of the lesson and they are encouraged to make efforts to achieve it. The clearer the purpose of a work, the more inspiring it is and the more dedication and devotion a person does.
(5). Principle of Planning
Be it teaching or any other work, its completion depends on whether the work is planned or not. While teaching, every teacher should make his/her teaching plan, the sequence of its presentation should be known so that the learner does not get confused as to what the teacher taught today. In the present teaching work, every trainee is given emphasis on making lesson plan and practicing it. A skilled teacher pays special attention to the interests of the children while determining the teaching methods. For this, while selecting the subject matter of teaching, he closely observes the wishes and needs of the child.
(6.) Principle of Selection
If we are ill, if we have to go to the doctor or even go to school, we will choose whatever is most important at that time so that the long-term impact is in our favor. This situation is called selection. Teaching is also a complex task, in which we have to study and understand various subjects. According to the principle of selection, useful elements to be used in teaching should be selected and useless elements should be left out. In a case, only those elements or subject materials should be taken, so that the objective can be achieved within time and successfully. While selecting subjects, the teacher should pay attention to the following things-
1- The amount of subject material should be such that the objective can be achieved.
2- The subject material should be according to the interest and ability of the students.
3- Should be finished within time.
4- The subject matter should be useful for life.
(7). Principle of Division
This is also called the principle of small steps. Teaching itself is a comprehensive process. The easiest way to make it successful is to teach it by dividing it. The teacher should divide the subject matter and proceed from simple to difficult so that consistency is maintained and communication remains practical. While making ‘Lesson Sutra’ of any lesson, we make many steps like introduction, purpose, statement, presentation, generalization, experiment etc. For example, to give knowledge of grammar, we will first give knowledge of letters, teach how to form words, then show how sentences are made, and then explain their use from the grammar point of view.
(8). Principle of Revision
This principle emphasizes that any activity or subject matter should be repeated several times before it is learned and assimilated. Due to this, the knowledge of the subject becomes durable and useful. Thorndike has called this the rule of practice. You all must have often heard this phrase – “Karat karat abhyas ke jadmati hota sujan! Raspi aavat jaat hai sil par par layer nishan” It means that the work which we do again and again, becomes easier. In teaching, the lesson or element which we read and teach again and again, we have a good grip on it and our interest and attention is also focused on it.
(9). Principle of Creation
Successful teaching is that which develops the creative power of children. For this, the teacher should encourage children to do such activities in education which are creative. In these creative activities, the brain, hands and heart of the children are combined. Due to this, he takes sufficient interest in the subject, because the burden of the subject does not fall on any one part. In the ‘Kindergarten’ and ‘Montessori’ methods used for children, children are given ample opportunity to create. Presently all modern teaching methods respect this principle.
(10). Principle of Individual Differences
Every child is different from each other in his interests, physical, mental conditions and abilities. This is called individual variation. In a class, there are some mentally retarded children who take a long time to understand the subject and there are some students who understand the subject only after a little prompting. Teachers should always keep these two types of students in mind, otherwise the teaching will be understood by some students and not by others.
(11). Principle of Previous Knowledge
According to this principle, children should be given knowledge of any new subject only on the basis of their previous knowledge. The new knowledge given to the child related to what he knows is permanent. For example, in the class the children have to be told about the deer, but the children have never seen the deer. The body structure of a goat is very similar to that of a deer and the children have also seen a goat, so in such a situation, if the teacher introduces the deer on the basis of the goat, then the children will be able to know well about the deer.
(12). Principle of Linking with Life
Education is a lifelong process. Human life can be improved only through education. Therefore, in the National Curriculum Framework 2005, emphasis has been laid on connecting education with life. The work of imparting education is done through teaching, while teaching any lesson the teacher should focus on those facts and aspects which connect the student to the activities of his life. Once this relationship is established, the new knowledge or skill becomes a permanent part of the child’s life and he uses this knowledge to solve the situations that arise in life. This principle is completely followed in all new teaching methods.
(13) Principle of Correlation
While teaching any subject, it should be taught by connecting it with other subjects; For example, teaching science by connecting it with geography, history, music etc. makes education interesting.
(14) Principle of flexibility
The education process should be creative and student friendly, that is, education should be flexible according to the circumstances and elements.
(15) Principle of Child Centered Education
Education can become effective only when it is organized according to the needs, abilities, interests and mental level of the students etc.
(16) Principle of Democratic Behavior
For the development of qualities like free expression, development of self-confidence, self-respect etc. in students, democratic behavior should be adopted instead of political behavior.
Teaching strategies are the methods and techniques that a teacher will use to support his or her students through the learning process; A teacher will select the most appropriate teaching strategy for the topic being studied, the learner’s level of expertise and the stage of their learning journey.
In one lesson, a teacher may use many different teaching strategies with different end goals. The most effective teaching strategies are those that are proven to work on large-scale tests. There is no need for any teaching strategy to be innovative.
- Know your students and develop respect for them
It may seem basic, but the foundation of all good teaching is an understanding of your students and their learning needs. It’s about respect between you and your students. The relationship between teacher and student is an important element of the learning experience. Remembering names, taking the time to get to know the new class from day one, and understanding what motivates them and their barriers to learning – this is an often overlooked teaching strategy.
- Appropriate use of summative and formative assessment
Summative assessment refers to assessment that occurs after the completion of a block of work, whether it is a unit or a school year. These are best considered as assessments of learning.
Formative assessments are those that occur day-to-day and are used to measure students’ understanding of a subject – they are assessments for learning. Formative assessment is often used in a diagnostic capacity to help us identify whether students are struggling with a subject at the moment. It can then guide and adapt our instructions during lessons to better meet children’s needs.
- Teach vocabulary
With the new focus on knowledge organizers in the curriculum, there is no excuse for children to miss out on relevant subject vocabulary. They need words to be able to form thoughts and sentences to talk confidently on a given topic.
That’s why our teachers will always pre-teach important maths terminology with their students at the beginning of the lesson, explaining any new terms and checking understanding of terms previously covered.
- Clear instructions
Also known as direct instruction, this teaching strategy is teacher-led and focuses on persistent questioning and guided practice to help students learn a subject. The backbone of explicit instruction is the use of a worked example in an example-problem pair. It involves silently displaying a worked example in its entirety along with a problem which students will then attempt to solve.
- Use of effective techniques
While we are all aware of the importance of asking questions as a tool to gauge students’ understanding of a topic, there are surefire techniques to improve the effectiveness of your questioning in the classroom.
“Are you sure?” Questions like “How do you know?” Encourage students to engage in grade-level-appropriate critical thinking to establish how confident they are in an answer and why, while asking others such as “Is there another way?” Help highlight where multiple methods may exist to achieve a solution.
Our teachers encourage students to express their reasoning verbally and ask questions to make sure students really have a grasp on the topic: “How do you know the answer is correct?”, ” Can you tell me how else you can solve this?” or “What is the first thing you need to do to answer this question?” These are all questions that come up again and again during our lessons.
- Constant practice
One of the most effective ways to introduce new concepts into a classroom, deliberate practice involves breaking learning into a series of subskills, each of which is deliberately practiced in turn.
- Fair discrimination
More than just “dividing the whole class into smaller groups based on achievement”, positive and effective differentiation at the primary school level can be difficult to achieve – poor differentiation strategies actually risk widening the gap we see. Trying to close.
But there are many effective differentiation strategies; Techniques such as interleaving and stepped learning as well as mathematics manipulatives and formative assessment are among the techniques that have beneficial effects on students when employed correctly.
- Strengthen efforts
Helping students make the connection between putting effort into a task and receiving recognition is an important step in developing a classroom environment that promotes active learning.
It does just that to encourage students to put more effort into activities, it does nothing to provide them with the motivation to do so. Praise and recognition are motivators with which students are already familiar; Moving them from being perfect to giving full effort can be highly effective.
- Metacognition
Literally “thinking about thinking”, metacognition has been found to be one of the most effective, lowest-cost teaching strategies, with students making an average of an additional seven months of progress.
Metacognition in primary schools often incorporates some other effective teaching strategies, such as asking questions in class – “How do you know?” Not only are students asked to justify their solutions, but they are also asked to think about their own thought processes in arriving at that solution.
- Personalized learning
This may seem obvious, but students are more likely to engage in learning when it is more targeted to them and tailored to their interests! This may be difficult to achieve at first – especially with larger classes of 30 students – but as familiarity and rapport increases throughout the year, it should become easier to make activities and even questions more personalized to individual children. Needed
- Collaborative Learning
Also called “cooperative learning,” the idea of having students work in groups for certain classroom activities will not be new to most teachers. A popular technique to foster this collaboration is through think-pair-share.
However, the impact of group work can vary widely, and to make it most effective, teachers should focus on well-structured tasks that promote interaction and interaction among students.
12- Student Center Education
The entire education system should actually be based on keeping the student at the center so that the overall development of the student can actually take place and the interests of the students are protected through education.
Meaning of Educational Technology
Educational Technology means teachers use educational and scientific techniques to make their teaching effective, interesting and easy. That technology is called ‘Educational Technology’.
Education can be made available to every student through technology. In which resources like internet, computer, teaching machine, television are used. Compared to earlier times, digital technology is used in today’s classes. Through which every student can feel free to ask answers to questions related to every subject through the teacher. Educational technology provides convenience to both teachers and students.
Educational technology is a systematic and organized process of applying modern technology to improve the quality (efficiency, optimum, truth, etc.) of education. It is a systematic way of conceptualizing the execution and evaluation of educational process, learning and teaching and helps in the application of modern educational teaching techniques. It includes instructional materials, methods and organization of work, and relationships, that is, the behavior of all participants in the educational process. The terms teaching resources are commonly used, although they are not synonymous (Pedagoski Lech-Sikon, 1996). The word technology is derived from the Greek word techno which means desire, skill, knowledge of the way, rule, skill, tool. Single word for educational technology. Various in different countries as educational technology, educational tools, resources, techniques of teaching. Use words and synonyms.
How many types of Educational Technology are there?
Educational technology was divided into three parts by American psychologist “Arthur Allen Lumsdaine”. He was a researcher in media uses and education studies. Let us know about the three types of Educational Technology.
- Hardware Approach
Hardware has been given the first place in educational technology. In this, emphasis has been laid on the assistive devices used in imparting education. It is also called ‘machine technology’. Besides, technology is also used in education.
Hardware Educational Technology includes accessories like projector, digital white board, slide projector, TV and monitor, computer, calculator, printing machine. Which are touched by hand.
- Software Approach
Just as the machine is used in the hardware approach. Similarly, Software Approach is based on the principles of learning and teaching. That is, which psychological principles (to know the mind of the student) do the teachers use for the mental development of the student.
Due to which necessary changes can come in the students. These are added to the software approach in educational technology. It is also called Technology of Education.
- System Approach
System Approach involves handling a complete system using educational technology, both hardware and software. In which all the resources used in teaching have to be used.
Such as using Projector, Chalk, digital whiteboard in the classroom in hardware approach and using Videos, Slides, Computer Program, charts etc. for a system in software approach. This is called ‘Educational Technology’. In which every system is managed in a systematic manner. Which is made up of both hardware and software.
Objectives or needs of educational technology
The objectives of educational technology are as follows:
1- Determining the objectives of education.
2- Identifying the educational needs and desires of the community.
3- Designing and developing curriculum related to arts, science and human values.
4- Preparing devices that support educational goals.
5- Managing the entire education process from planning to execution, implementation and evaluation.
6- Defining and writing these objectives in practical terms.
7- Analysis.
8- Modernizing the teaching-learning process.
9- To prepare educational technology models to improve the existing process of teaching and learning.
10- To expand and support educational opportunities for people around the world, especially marginalized sections of the community.
11- Analyzing the text and setting the elements and components in an order.
12- To improve the teaching-learning process.
13- To increase the qualifications and capabilities of teachers by training them.
14- To analyze the qualities, abilities, achievements and skills of the students.
Importance of Educational Technology
In the 21st century, due to the integration of educational technology, the landscape of education is undergoing profound change. We will explore the importance of educational technology and how it is revolutionizing learning in the digital age.
- Solution of geographical barriers
One of the primary benefits of educational technology is its ability to break down geographical barriers. Through online learning platforms and virtual classrooms, students from different corners of the world can access the same high-quality education. This democratization of education ensures that individuals, regardless of their location, have equal opportunities to learn and acquire valuable skills. This not only promotes global collaboration but also brings diverse perspectives into the virtual classroom, thereby enriching the learning experience.
- Personalized learning opportunities
Educational technology enables personalized learning experiences tailored to individual student needs. Adaptive learning platforms use algorithms and data analytics to assess a student’s strengths and weaknesses, adjusting the pace and content of lessons accordingly. This ensures that students can understand concepts at their own pace, promoting a deeper understanding of the material. Personalized learning also caters to different learning styles, accommodates visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners, and promotes a more inclusive educational environment.
- Increased participation through multimedia
Traditional textbooks are gradually being replaced by interactive multimedia content, making learning more engaging and dynamic. Educational technology allows for the inclusion of video, simulation, virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR) in the curriculum. These multimedia elements capture students’ attention, making complex concepts more accessible and entertaining. As a result, students are more likely to retain information and develop a genuine interest in the subjects they are studying.
- Application of knowledge in real form
The integration of educational technology fosters a bridge between theoretical knowledge and real-world application. Simulations and virtual laboratories provide students with practical experience in a controlled and safe environment. For example, medical students can practice surgical procedures in virtual reality, and engineering students can simulate complex projects. This practical application of knowledge prepares students for the challenges they will face in their future careers, promoting a more seamless transition from education to the workplace.
- Facilitate collaborative learning
Educational technology facilitates collaborative learning that overcomes the limitations of physical classrooms. Online forums, collaborative documents, and video conferencing tools enable students to work together on projects and assignments, promoting teamwork and communication skills. This not only reflects the collaborative nature of many business environments but also exposes students to diverse perspectives and ideas. Collaborative learning prepares students for a world where teamwork and effective communication are essential skills.
- Continuous evaluation and feedback
Traditional methods of assessment, such as exams and quizzes, are evolving with the help of educational technology. Online platforms allow continuous assessment through quizzes, interactive assignments and real-time feedback. This ongoing assessment provides teachers with valuable insight into individual student progress, allowing timely intervention when needed. Furthermore, it focuses on more comprehensive and continuous assessment of student understanding and performance than one-time, high-stakes assessment.
- Global access to educational resources
The digital age has ushered in an era of unprecedented access to educational resources. Online libraries, open educational resources (OER), and digital archives make vast amounts of information available to students and teachers around the world. This democratization of knowledge ensures that financial barriers and geographical location will no longer be a barrier to accessing quality educational content. Students can discover a wealth of information beyond their textbooks, fostering a culture of self-directed and lifelong learning.
- Development of capabilities with the help of technology
As technology is becoming an integral part of various industries, it is important to incorporate educational technology into the curriculum to prepare students for the workforce. Being exposed to coding, digital literacy and emerging technologies equips students with the skills needed for the jobs of the future. Educational technology not only enhances traditional subjects but also introduces students to tools and technologies they are likely to encounter in their chosen fields, giving them a competitive edge in the job market.
Teaching skill is that quality of a person through which a person becomes a good teacher. If understood in simple words, Teaching Skills means the art of teaching. A teacher should have good teaching skills, only then he can teach children properly and make their future bright.
Teaching skill is an important skill that provides us with the ability to pass on knowledge and experience. In teaching skills, the skills of teachers are improved so that teachers can provide high quality education. Good teachers not only impart knowledge but they also provide their students with the ability to think, understand and communicate.
Through good teachers we can provide positive and interview based education to the students. They guide the students through their high standards, competence, and inspirational personality. Having good teaching skills is essential in education and it contributes significantly to the development of our society.
Definitions of Teaching Skills
In the words of N.L. Gage
‘Teaching skills are those specific instructional activities and procedures, which the teacher uses in the classroom to make his teaching effective. It is related to different stages of teaching and is in constant use by the teacher.
According to Dr. B.K. Pasi
“Teaching skills are a set of related instructional activities or behaviors designed to facilitate student learning.”
Characteristics of teaching skills
As a result of the discussion of the above definitions, the following characteristics of teaching skills are visible –
(1) Teaching skills are related to teaching processes and behaviours.
(2) Teaching skills are related to the unit of classroom teaching behavior.
(3) Teaching skills are helpful in achieving specific goals of education.
(4) Teaching skills make the teaching process effective.
(5) Through teaching skills, subject matter can be taught to students easily and easily.
(6) The entire interaction is made active through teaching skills.
Teaching Skills helps teachers to provide a successful and effective education. A good teacher not only imparts knowledge to students but also provides them with the ability to solve problems, communicate actively, and think independently. Therefore, professional development of teaching skills is of utmost importance for teachers.
1- Important role in the development of students
Effective use of teaching skills plays an important role in the proper and holistic development of students. The education given by teachers not only provides knowledge and official information to the students, but also gives them a path to dedicate themselves with new thinking.
2- Encouraging activism
Teaching skills encourages an active and lucky learning process. A good teacher encourages students to exercise their innate abilities and provides them with the inspiration to move ahead in life through education.
3- Motivate students
Good teachers always motivate students and lead them towards success through education. An inspirational teacher provides the highest level of education, inspiration and guidance to the students.
Teaching skills have great importance in the field of education. It plays an important role in the development of students and provides them inspiration. A good teacher gives right guidance to the students and leads them towards a successful and verified life.
4- Achievement of learning objectives
In fact, through teaching skills, the teacher’s objectives are achieved very easily. Because through teaching skills, the skills of the teachers are worked upon with great intensity and as a result the teaching work is completed with meaning.
5- Interestingness in the teaching process
Teaching skills add interest to the entire teacher’s work because as a result of teaching skills, teaching activities are carried out with practicality.
Micro-learning is made up of two words – micro and teaching. Micro means small (intensive) and teaching means the teaching given in the classroom during training. Microteaching is a teacher training technique whereby a teacher reviews a recording of a teaching session to receive constructive feedback from students about what work they have done during teaching. And what improvements can be made in their teaching techniques?
Microteaching was invented by Dwight W. Allen at Stanford University in 1963, and later used to develop teachers in all forms of education.
Microteaching is a technique aimed at preparing teacher candidates for real classroom settings. With the help of this technique, the teacher candidate attempts to learn each teaching skill by breaking it into smaller parts and without crowded classrooms. During micro-teaching, skills of presentations and demonstrations are developed to actively interact with students while inculcating teaching skills in them.
Wilkinson, emphasizes that the teacher candidate experiences actual teaching and learning rules with the help of this method. This method provides teachers with opportunities to explore and reflect on their own and others’ teaching styles and enables them to learn about new teaching techniques.
Micro teaching is a cycle in teaching in which the student teacher gives a presentation of her subject in a cycle in front of her classmates and the invigilator.
In the cycle of micro teaching, all the six stages which form a cycle are called the steps of micro teaching. The steps of micro teaching are explained as follows:-
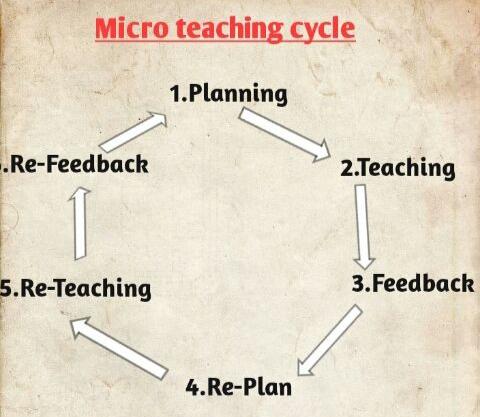
1- Make a plan
This is considered to be the first step of micro teaching, under this the student teacher or student teacher prepares the subject for his/her readers, for this he/she can get information about his/her subject matter and can prepare a plan sitting at home.
2- Teaching
The second step of micro teaching is teaching, under which whatever reader subject has been prepared by the student teacher or student teacher, the student teacher or student teacher teaches/presents it in front of their classmates, teacher and invigilator.
3- Feedback
Feedback is the third step of micro teaching, in which what are the shortcomings in the presentation of the subject given by the student teacher to her readers? What other improvements need to be made in it? This is what his classmates, teachers and inspectors tell him. If the surface nutrition is positive then the subtle learning ends here, but if it is negative then the fourth step of planning comes again.
4- Re-plan
The fourth step of micro teaching is re-planning, under which the student teacher or student teacher plans and prepares the subject on the basis of the suggestions given by her classmates, teacher and invigilator at the same time.
5- Re-Teaching
Re-teaching is the fifth step of micro-teaching, under which the student teacher again presents the subject prepared in the plan to the classmates, teacher and invigilator.
6 Re-Feedback
Re-feedback is the last step of micro teaching i.e. the sixth step, under which what mistakes have been made in the re-teaching i.e. re-presentation given by the student teacher and the student teacher? What else needs to be improved? This is again determined by their classmates, teachers and class invigilators.
Simulated social skill training method
Through this method, training of certain behaviors is given in artificial circumstances. In this, teaching skills are trained in a dramatic form and different people have to play different roles, due to which this is accomplished in a dramatic form in the form of the entire education system. Students have to perform a variety of roles for teacher training in a simulated classroom environment.
It is actually a parenting technique, which through role playing, certain desired social skills of the teachers are developed in the students in artificial situations in the classroom and in their own group.
Characteristics of Simulated social skill training
- With the help of this method, student teachers are given effective support.
- Student teachers are given opportunities for pre-practice teaching before sending them to the classroom.
- Through this method, knowledge and skills of general behavior are developed.
- It can be used as a method of research.
- It is more useful for student teachers. In this they can fundamentally develop their teaching skills.
- Without school teaching, students get opportunities to teach like school (simulation), due to which they learn and take interest in teaching.
- The teacher tries to solve the problems arising in actual teaching by teaching through simulation.
- In simulation teaching, the student teacher acquires expertise in various teaching skills due to which he can do the actual teaching easily.
- Using this method increases self-confidence among student teachers. The ability to present the subject matter in a systematic manner develops in the student teachers.
- First of all, student teachers are divided into small groups according to different subjects.
- It is ensured that all the student teachers have undergone micro-teaching and have thoroughly learned the skills of teaching.
- Five to eight student teachers are kept in a group.
- Student teachers are taught to make lesson plans for their subject.
- After preparing the lesson plans, they are inspected by the teacher.
- After correcting the errors identified during inspection, the student teacher prepares the lesson plan.
- After completely preparing the lesson plan, every student teacher has to do simulation teaching sequentially.
- The teacher marks the mistakes of the student on the lesson plan and praises the correct work.
- Student teachers practice to correct those shortcomings.
- Again in the presence of the teacher, simulated teaching is done by the student teachers one by one and supervised by the teacher.
- This sequence of simulated teaching continues till then. Unless the student teacher corrects the errors being made in teaching.
Advantages of Simulated Teaching
- This gives the student teacher knowledge about the classroom situation he will face in the future.
- Through simulated teaching, the student learns how he has to behave in the classroom in future under what circumstances.
- By doing simulated teaching before actual teaching, there is no fear or doubt in the mind of the student teacher.
- In simulated teaching, the teacher makes video or audio recording of the teaching being done by the student and by showing or narrating that recording to the students, he can tell the errors made by the student and correct them.
- The student teacher does the teaching work in short periods of time and at the same time he continues to get support due to which the students remain active.
- This provides an opportunity to develop various skills in the student teacher.
- The self-confidence of the student-teacher increases.
- Problem solving ability develops in the student teacher.
- In this education the child plays different roles. It works, hence he can make himself successful in any role and work in the practical world.
- It reduces the gap between teaching theory and practice.
- According to Bruner, simulation is helpful in bringing deeper understanding into the mind.
Limitations of Simulated Teaching
- This technique cannot be used in small classes.
- Associate students act as students of lower classes who are not able to respond like real students.
- Student teachers are not able to teach with full confidence in front of their fellow students.
- Due to lack of competent and dedicated teachers, tailored teaching is not carried out effectively which requires more teachers who are not available.
Concept of Feedback in Teacher Education
‘Feedback’ means providing information to students about their performance in relation to a specific learning objective and providing guidance on how they can improve or move forward.
Feedback serves as a powerful tool in the field of education, playing a vital role in shaping learning experiences and promoting their academic growth. Recognizing the importance of feedback and implementing effective feedback mechanisms can lead to enhanced learning outcomes, improved performance and increased motivation among students.
Importance of feedback in teacher education
Feedback is a two-way communication process that provides students with valuable information about their strengths and areas for improvement. It acts as a guiding light, helping students pursue their educational journey with greater clarity. Timely and constructive feedback not only reinforces learning but also creates a sense of accountability and responsibility in students, enabling them to take ownership of their progress.
- Identifying strengths and weaknesses
Feedback highlights the strengths of students, encouraging them to perform better. Additionally, it highlights areas that need attention, and provides a roadmap for targeted improvements.
- Developing capabilities
Constructive feedback helps students gain a deeper understanding of their abilities and areas that need development. This self-awareness empowers them to set realistic goals and formulate their own learning strategies.
- Encouraging critical thinking
Feedback motivates students to critically analyze their work. They learn to evaluate their thought processes, decision making and problem solving skills, thereby enhancing their ability to think independently.
- Motivate for continuous learning
Positive feedback acknowledges students’ efforts and achievements, increasing their confidence and motivation. In contrast, constructive feedback promotes determination to overcome challenges and strive for growth.
- Promote effective communication
Receiving feedback teaches students how to receive information graciously, listen actively, and participate in meaningful dialogues. These skills are essential in both academic and real-world contexts.
- Customizing learning experiences
Teachers can tailor instruction based on feedback to accommodate different learning styles and paces. This individualized approach ensures that students receive the support they need to excel.
Flander’s interaction analysis category system
The interaction analysis method started in 1930. Ned A. Flanders (1951) made a special contribution in analyzing classroom behaviour. Ned A. Flender (1960) gave a learning model based on interactions, which is also called end-process learning model or social end-process model. Flander has considered the teaching process as an end process. In this model, the teaching process is considered to be an interaction between teacher and student regarding a subject in a particular social environment.
Teacher’s behavior has a great impact on students’ learning. After this, academics worked on measuring behavior. He thought that if we find out how much teacher behavior is related to students’ learning, then teachers can be trained for learning. Flander’s name was notable in this mission. He created a tool to measure teacher’s behavior which was named ‘Flanders Classroom Interaction System’. It represents verbal interaction in the classroom. He says that if verbal behavior can be measured then there is no need to measure non-verbal behavior. They say that in the class either the teacher or the student speaks or both remain silent.
With the help of this technique, events occurring within three seconds or less are monitored systematically. This is an objective and scientific observation method. Through this, the behavior of the class has been divided into two parts, which is being displayed as follows.
(a) nonverbal behavior
This is the behavior in which there is no verbal exchange of ideas between the student and the teacher, rather the teacher asks the students to do or not do something through his body language, for example, shaking his head or looking angry.
(b) verbal behavior
This is the behavior in which teachers and students exchange their ideas by speaking on a topic. The verbal behavior of the teacher can also be divided into two parts depending on the amount of freedom the teacher provides to the students in the classroom.
(1) Indirect verbal behavior
Indirect verbal behavior occurs when the teacher praises and encourages students. Flanders has called a teacher with this type of behavior as an indirect teacher. Anderson has called it ‘appropriate teacher’, Lippitt and Height have called it ‘democratic teacher’ and Widhall has called it ‘student-centered teacher’. In this behavior teachers provide maximum opportunity to students to speak. It has been found through tests that indirect teachers are cheerful, brave, trustworthy and give advice and this kind of behavior is more helpful in the learning and character development of the students.
(II) Direct verbal behavior
Direct verbal behavior occurs when teachers do not give students the opportunity to speak and maintain dominance in the classroom. Flanders has called a teacher with this type of behavior a ‘direct teacher’, Lippitt and Height have called him a ‘non-democratic teacher’ and Widhal has called him a ‘learning-centered teacher’.
FLANDERS TEN INTERACTION ANALYSIS CATEGORY SYSTEM
(1) Accepts Feelings
Naturally accepting and giving importance to the feelings and thoughts of the students. These thoughts, feelings or experiences can be in the form of negative, positive, memories and predictions.
(2) Praises and Encouragements
Activities include praising student behavior and actions, motivating them, making jokes in between to remove tension in the class, etc.
(3) Accept or Uses Ideas of Students
Clarifying and restating the ideas expressed by students.
(4) Ask Questions
Asking questions to students on the subject matter taught.
(5) Lecturing
The teacher explains the facts by expressing his own views on the curriculum process.
(6) Giving Direction
Giving orders and instructions etc. to students, which students are expected to follow.
(7) Criticism
Criticizing to control inappropriate behavior of students.
(8) Student Talk Response
Students react to the actions taken by the teacher and the instructions given.
(9) Pupil Talk Initiation
In this, the student solves his curiosity by asking questions.
(10) Silence/Confusion or Noise
Sometimes in the class all the students and the teacher speak, sometimes there is complete silence in the class.
Procedure of Flanders Interaction Analysis
Two main processes are carried out in this interaction:
- Marking Process
In this process, the inspector should have good knowledge of the ten categories mentioned on the inspection form. For this, the guidance and supervision of an experienced inspector is also necessary. In this, the inspector should have the ability to give suggestions along with practice. It is necessary to record events of up to 3 seconds in class. In this the observer remains active in recording all the actions and events. In this technique, emphasis is laid on accuracy of marking. It is necessary that the lesson should be observed for at least 20 minutes and 400 frequencies should be recorded in one observation. A sample of the inspection matrix is presented here.
- Notation process or interpretation process
The data obtained from the scoring process is analyzed and interpreted, through which the teacher’s behavior is analyzed. For this, mainly explanation is given in two forms – quantitative and qualitative.
(a) quantitative explanation
For quantitative interpretation, class ratio, behavior ratio and interaction variable are followed, for this various formulas are taken. Here formulas are being presented in relation to the number of ten categories.
(b) qualitative explanation
Analysis and interpretation of classroom behavior is done quantitatively as well as quantitatively. For this, flow chart, flow diagram and interaction model are followed according to the clock. Whose brief description is being presented here.
- Clock wise flow chart
The data obtained from quantitative interpretation is plotted in a clock-like chart. First of all, the orbital with maximum frequency in the matrix is detected. A circle is drawn around the frequency of this orbital. goes . This is the starting point of orbital flow. After determining the starting point, the event to occur is traced and circled. After that, an arrow point is made from the first sphere and joined to the second sphere. Now the orbital with maximum frequency is seen in the second row of this orbital and a circle is drawn on it and it is joined with the circle of the second orbital by an arrow.
In this way, almost all those cells which have high frequencies are circled and included in the flow. In this process it is generally decided what should be the lowest frequency? This cycle continues until certain frequencies are included in that flow cycle.
- Manjusha diagram
It is difficult to understand the teacher’s behavior through the flow chart according to the clock, hence the classroom behavior is recorded separately through the Manjusha flow chart. In this, squares and signs are made small, big, thick and thin, like, (-> -> ->) The mutual actions of the student and the teacher are clearly marked. In its structure, the steady state orbits of the teacher and the student are shown separately – one is called the teacher’s statement and the other is the student’s statement. The class of each steady state orbital is made smaller or larger keeping in mind its frequency. In this, the limit of frequencies of steady state orbitals should be determined. Cells with frequencies higher than that should be included in the flow chart.
- Interaction Model
Flanders developed the interaction model for the qualitative explanation of teaching behavior. In this, teaching behavior is explained in terms of results. External verbal behavior is expressed with the help of a matrix (total frequencies) of learning responses in a prescribed sequence according to the flow theory. The interaction analysis model is an objective technique of interaction analysis. In this, events up to three seconds are recorded and analyzed. In this, pure representation of teaching format and teacher behavior is done. There is expression in form. The interaction model is mainly divided into two parts. Flanders has developed the interaction-related teaching model which presents the teaching format, but does not give much emphasis on non-verbal interaction, whereas non-verbal interaction is equally important in teaching as verbal interaction. Is.
Features of interactive learning model
(i) In this the teaching flow is according to the principle.
(ii) External verbal behavior can be explained in this teaching model.
(ii) Teaching behavior is related to certain educational outcomes.
(iv) A definite sequence is followed in the responses of teaching.
(v) Specific learning behavior can be demonstrated with the help of array.
Limitations of the interactive learning model
(i) No decision regarding the subject matter can be taken in this model.
(ii) In this the non-verbal end process cannot be analyzed and observed.
(iii) The nature of teaching is narrowed down by dividing the behavior of teaching into ten categories.
(iv) In this, a situation of imbalance is also seen by dividing teaching behavior and student behavior into two categories.
(v) It is difficult to mark the end process in this.
Thus, in the end process teaching model, teachers can find out how their behavior or teaching is impacting the class by analyzing the interactions.
The materials which the teacher uses while explaining the course material while teaching are called teaching aids.
(1) print material
Print material is material that is available in printed form. Such as book, magazine, pamphlet etc.
(2) audio material
Audio materials are those materials which can be heard through ears. Such as USB drive, cassette, microphone, tape recorder, etc.
(3) visual material
Visual materials are those means which we can see through eyes. Such as chart paper, real objects, maps etc.
(4) Audio-visual material
Audio-visual materials are “those means which we can see with our eyes and hear their related sounds with our ears. The processes in which visual and audio senses actively participate are called audio-visual means.” Like movies, TV, drama, YouTube etc.
The importance of teaching aids is as follows-
1- Helpful in learning and understanding
When teaching aids are used in teaching work, it is natural that students’ understanding increases and it becomes easier for them to learn.
2- Interestingness in lesson material
A lesson is presented in a very attractive way through teaching aids. Due to which the entire lesson material gets interesting.
3- Effectiveness in lesson
When a teacher uses teaching aids while teaching in the class, the lesson becomes effective.
4- Simplicity in text display
As a result of teaching aids, lesson demonstration becomes easier and students understand well through it.
5- Focus of students
When the entire teaching is done with great significance through teaching aids, then the objectives of teaching are easily achieved because through this, students’ attention is focused towards teaching, which is actually a good teaching. It is necessary for.
6- To awaken interest in learning
Through teaching aids, students are encouraged to learn all the time because through teaching aids, the entire teaching system is made interesting and every possible student is encouraged to learn.
7- Making learning active
Teaching aids are used to make teaching actually useful for learning in a way that can be implemented in real life. With the help of these supporting materials, the student tries to relate what he has to learn to its actual form.
Role of ICT for effective teaching
The use of ICT by teachers in their teaching practices can range from essentially minor enhancements to traditional methods of teaching, to more fundamental changes in their approach to teaching. ICT can be used to reinforce the prevailing pedagogical practices as well as to strengthen the way of communication between teachers and students.
ICT stands for Information and Communication Technology. Over the last few decades, ICT has become indispensable to our lives which affects individual lives as well as our society. It has changed many aspects of life, leading to a rethinking of the roles, pedagogy and approach of educational institutions, administrators and teachers. Teachers use ICT to make teaching and learning effective and interesting. In the modern era, education demands more knowledge of ICT and skills of using ICT for the teacher in the teaching-learning process. This paper focuses on the role of ICT in 21st century teacher education. Nowadays ICT is giving a new look to schools and classrooms and also providing more facilities to teachers and students. ICT also helps teachers, students and parents come together. Therefore, knowledge of ICT is very essential for both pre-service and in-service teachers, which helps teachers to integrate technology in classroom teaching.
The role of information and communication technology is very important in effective teaching, under which the teacher can be improved further. The role or importance of ICT in effective teaching is as follows-
- To promote the quality of teaching
- Making the curriculum learning centric
- Personalized and flexible learning
- Inclusion of Vocationalization in Teaching
- Encourage self-learning among students
- Change in examination system through ICT
- Changes in assessment through ICT
- Access to information and resources
- Use of attractive teaching methods
- Cooperation and global relations
- Inclusive education
Meaning of innovation in teaching
“Innovation in Education” This refers to the introduction of new and inspired ideas, products, technologies and innovations for positive change and improvement in the field of education. This theory promotes the development and implementation of innovative approaches to teaching and learning.
Innovation in education is not just a slogan. The education landscape is witnessing a transformational shift towards more dynamic and personalized learning experiences. These changes are driven by a blend of technology and a deep understanding of human needs.
Need for innovation in teaching
Education has come far beyond the traditional classroom setting and rote learning. Today, the learning landscape is evolving at an unprecedented pace, and it is important to keep pace with these changes. Innovation in education is the key not only to keep pace with this growth, but also to move ahead.
1- Innovation is necessary to raise the level of education.
2- Innovation in education is necessary for social change.
3- There is a need for innovation in education for the economic development of the people.
4- Innovation is necessary for interesting education.
5- Innovation is necessary to bring positive behavior in teachers.
6- To establish a welfare state
7- Education system in accordance with scientific and technological progress
8- To develop human resources
9- To increase employment opportunities
10- To solve the problems caused by environmental pollution
11- To increase specialization and meet the problems arising from it.
Importance of innovation in teaching
The importance of innovation in teaching is in the following form-
1- Permanence of knowledge
Before the use of innovations in education, the knowledge gained by the students was forgotten after some time, because the students did not have an active role. With the use of innovations, students were kept fully active so that they do not forget the knowledge gained quickly. Therefore, the use of educational innovations is very important for the sustainability of knowledge.
2- To achieve educational objectives
To achieve educational objectives, innovations emerged and the path to achieving educational objectives became easier.
3- For use of teaching learning material
In ancient times, monotony used to arise in the teaching-learning process. As a result, the need for innovation was felt. With the use of innovations, technical means have started being used on a wide scale in teaching learning material.
4- For all-round development of students
Innovations play an important role in the all-round development of students. In ancient times, full attention was given to developing the cognitive aspect of the learner. At present, the inherent talents of the students are known and full efforts are made for their development. This work is done through co-curricular activities. In this, the potential and development possibilities of various talents of the students are known. After this, arrangements are made for their development.
5- For development of skills
Micro Teaching is the main method of innovation. In this, many types of skills are developed in student teachers. When these skills are developed, the teacher can teach the students effectively. These skills are often used in the teaching-learning process; For example, in introduction skills, the art of formulating introduction questions and presenting them is developed in the student teacher. In interpretation skills, the skill of giving effective, simple and understandable explanation of any fact is developed.
6- For knowledge of new teaching methods
Knowledge of new teaching methods is possible through the use of innovations. The credit for giving birth to the concepts of micro-teaching, instruction and team teaching etc. in the education system goes to innovations. Due to lack of innovations, all the teachers used to teach using ancient teaching methods which were faulty. Through innovations, teachers have now started using new teaching methods, which is benefiting both teachers and students.
7- Development of scientific approach
Scientific approach develops through innovations. By adopting new activities, scientific attitude develops in the teacher and the student.
8- To improve the education system
Innovations are used to improve the education system. There should also be changes in the education system as per the demands of time and society. Earlier students used to study sitting on seats in the shade of trees, today they study in air-conditioned classrooms. Necessary reforms were made in the education system through innovations.
9- For the development of research
Development of research in education is possible only through the use of innovations. Research work is conducted on problems related to teaching-learning process and other educational systems and the findings obtained from it are used in the educational system.
10- Solution to many problems
Five-year plans were implemented in India with a view to achieving rapid economic development and self-reliance. As a result of these schemes, there were radical changes in the agricultural and industrial system in our country. Due to these changes, new problems have arisen before the country. In which rapid population growth, urbanization, industrialization, environmental pollution, unemployment are the main ones in which the need to accept new dimensions, new trends or innovations in the system was felt.
11- For the effectiveness of teaching learning process
Use of innovations is necessary for the effectiveness of teaching-learning. In ancient times, the role of the teacher in the teaching-learning process was important and the role of the child was secondary. The learner used to listen to the teacher’s thoughts like a hungry listener. The need for innovations was felt to improve this system and the use of innovations resulted in effectiveness in the teaching-learning process.
When two or more teachers collaborate with each other and teach a particular subject to a group of students, it is called group teaching or team teaching. Teachers are experts in their respective fields. One of the teachers is the leader of the entire team who runs the entire system and the rest of the teachers work under his direction. The success of this teaching depends on the team leader. In this teaching technique, teachers teach on the basis of mutual cooperation, hence it is called team teaching.
Characteristics of Team Teaching
1- Collective Responsibility
All teachers involved in the team teaching approach share responsibility for the success of the instructional program.
Example: If students in a math class are struggling to understand a particular concept, in a team teaching approach all the teachers involved can work together to find a solution instead of leaving it to just one teacher.
2- Simultaneous Instruction
In team teaching, two or more teachers provide instruction to students in the same classroom at the same time.
Example: In a science class, one teacher may lead a lecture, while another teacher helps students with practical activities.
3-Thorough Planning
Team teaching requires thorough planning and organization in advance.
Example: Two or more teachers may meet regularly to plan lessons, create instructional materials, and discuss how to meet students’ needs.
4- Use of Visual Aids
Visual aids, such as multimedia presentations, charts, and diagrams, are often used in team teaching to increase student understanding and engagement.
Example: Teachers can use videos or images to help students better understand complex concepts.
5- Development of Cooperation
Team teaching promotes a culture of collaboration and mutual support among teachers.
Example: Teachers can share feedback and resources to improve each other’s teaching strategies.
6- Exposure to Different Areas
Team teaching provides students with exposure to multiple fields and subjects.
Example: A team of English and social studies teachers might collaborate to teach a unit on American literature and history, giving students a deeper understanding of how the two subjects are interconnected.
7- Involvement of Experts
In some cases, team teaching may involve the involvement of external experts, such as experienced teachers or subject matter experts.
Example: A science teacher might invite a scientist to talk to the class about his research.
8- Opportunities for Group Work
Team learning provides more opportunities for group work, allowing students to work according to their capabilities, abilities and interests.
Example: Teachers can assign group projects that cover different skills and knowledge areas.
1- Effective and qualitative teaching
Team teaching provides effective and high-quality teaching because it involves multiple teachers who can bring their expertise and diverse perspectives to the classroom.
Example: In a science class, one teacher can focus on explaining theoretical concepts while another demonstrates the experiment, leading to a more effective and engaging learning experience for students.
2- Improved classroom management
The problem of classroom management and discipline can be reduced by the presence of multiple teachers.
Example: If one teacher is handling a difficult student, the other teacher can continue the lesson while making sure the rest of the class stays on track.
3- Development of social skills
Team teaching promotes the development of high social qualities because it emphasizes group work and cooperation among students.
Example: In team learning, students are encouraged to work together in groups and this helps them develop better social skills like communication, cooperation and leadership.
4- Use of audio-visual aids
Team teaching allows the use of audio-visual aids that can enhance the learning experience and make it more engaging.
Example: One teacher may use a visual presentation while another teacher explains the material. This helps students to understand the subject better.
5- Promotion of competition
Through team teaching, a sense of competition can be promoted among students and teachers, which can motivate them to perform better.
Example: In a team teaching environment, teachers can collaborate and compete with each other to create more engaging and effective teaching methods.
6- Encouragement of group work
Team teaching promotes group work and collaboration among students, which can enhance their communication and social skills.
Example: In a history class, the teacher might divide students into groups to research different historical events and present their findings to the rest of the class, promoting teamwork and collaboration.
7- Following psychological principles
Team teaching is based on psychological principles such as social learning and cognitive development, which can result in more effective teaching.
Example: Teachers can use different teaching styles to meet the different learning needs of students, ensuring that everyone is engaging and learning at their own pace.
8- Opportunities for debates
Debate can be given a prominent place in team learning, providing opportunities for students and teachers to acquire new knowledge and develop their critical thinking skills.
Example: In a social studies classroom, teachers can encourage debate on current events or historical issues, leading to a deeper understanding of the topic for both students and teachers.
Limitations/Disadvantages of Team Teaching
1- Additional arrangements and funds
Team teaching requires additional arrangements and funding in school settings, which can be a burden on school budgets.
For example, if a school has to arrange for multiple teachers for one class, it may increase the overall cost of education.
2- Mutual cooperation and coordination
The success of team teaching is based on mutual cooperation and coordination among team members. Team teaching cannot be successful if there is a lack of cooperation among team members.
3- Absence of team members
Team teaching requires advance preparation. If one member of the team becomes absent, it may hinder group/team learning.
For example, if one teacher is absent, another teacher may have to fill in for the absent teacher, which can create additional workload.
4- Individual differences
Difficulty in team teaching may occur due to individual differences among team members.
For example, if one teacher’s teaching style or approach is different from that of another teacher, it may cause conflict in the team.
5- Additional financial burden
Team teaching may impose additional financial burden on school administrators.
For example, if the school has to hire additional teachers for team teaching or pay teachers extra salaries, this can add to the school’s expenses.
In India, teachers are considered as nation builders because teachers play the role of parents. Only teachers can foster student development, skills and creativity. Someone has well said that we all are well aware that the art of teaching is the art of helping in discovery. Teaching profession implies imparting knowledge and making a better individual with all the common forms of discipline. The teaching profession is strengthening career opportunities that contribute to the development of the country.
Importance of teaching as a profession
We can say that teaching profession is not just a job. The teaching profession is about shaping the future of our country. Therefore professional learning plays an important role in guiding our youth in the right direction and realizing their dreams.
1- Increase in teacher productivity
If teaching is developed as a profession, then the productivity of the teacher actually increases because the teacher will be fully engaged in conducting his teaching work, which will directly benefit the students and the productivity of the teacher will increase. also increases.
2- The teacher should be free from prejudice.
When a teacher will be completely sure about the job and will get salary in return for the teaching work, then there will be no doubt in his mind regarding his way of life and he will be free from all kinds of prejudices and will be able to carry on the teaching work. Will focus on doing.
3- To provide quality education to students
After a teacher is confident about his job, he conducts the teaching work without any tension, due to which he spends 100 percent time with the children to complete the teaching work, due to which it is natural that the quality of education will be better and the students will will be benefited.
4- Using the teacher to his full potential
After teachers do not have any tension about the job, a teacher conducts the work of teaching using his full capacity. To the extent of his own capacity, he uses all those capacities only and only for the teaching work because he has a job. There is no tension and he gets salary in return for his teaching work and earns his living from it.
5- Proper coordination between teacher and students
When a teacher gives his full capacity and 100 percent time to teaching work, then proper coordination is established between the teacher and the students. All this is possible when teaching is developed as a profession.
6- Encouraging other students towards teaching profession
When teaching is developed as a profession, it is natural that other students will also be encouraged towards this profession. People will be eager to come into this profession when the teaching profession is actually developed in this form.
Need for development of teaching profession
Nowadays teaching is the most desirable profession. The importance of teaching profession includes entertainment and learning together. Being in the teaching profession doesn’t mean you have to share your knowledge. Sometimes teachers learn something new from the teaching experience itself.
Teachers play an important role in the lives of students by helping them achieve their goals. Therefore, choosing teaching profession offers endless career opportunities. However, teaching is not the only profession; In fact, it is an activity to serve education.
Here we have listed some importance of teaching profession. Therefore, those who are interested in becoming a teacher must keep the following things in mind-
1- Improving communication skills
Teaching is a systematic technique of communicating to more and more people. Thus, being in the teaching profession will improve communication skills. As a result, the person can interact with others more confidently.
2- Increasing knowledge and skills
Teacher is the person who transmits his knowledge and skills to the younger generation. Through this profession, teachers inspire students to focus on and develop their natural abilities.
3- Yourself as a learner
Since there is no limit to learning, one can never stop learning. Even in the teaching profession, a teacher can learn at any level and age. RN Tagore has also said this.
4- Experience of handling different children
School or college is a place where different students with different mindset arrive. The teacher must have the ability to handle all children, whether normal, intelligent or physically handicapped.
5- Excellent organization skills
Teaching profession makes a person a multi-tasker; Despite imparting education to students, teachers and organizational skills. Being organized means that a person can manage time and resources efficiently and effectively for better productivity.
6- Ethical and disciplined
A characteristic of the teaching profession includes ethics and discipline. Teachers teach moral values which make students more disciplined. Ethical behavior encourages students to know what is bad or good for them.
7- Establishing a role model for others
Becoming a teacher is not very complicated but being liked by everyone matters. Teachers should motivate students to discover their hidden talents and achieve their goals. A motivated teacher can inspire students by setting role models.
professional ethics among teachers
Professional ethics for teachers is a set of guidelines and principles that guide their conduct and behavior, ultimately enhancing the dignity and status of the teaching profession. As nation-builders and teachers, teachers play a vital role in shaping the future of their students and society. To fulfill this responsibility, teachers must possess knowledge, skills, personal values, ethics, and commitment to their work.
The National Council for Teacher Education (NCTE) has outlined specific principles for teachers, emphasizing the right of every child to education and the importance of recognizing the inherent potential. Teachers should also promote a sense of holistic culture and national identity. Self-respect and professionalism among teachers is important, as they are an integral part of society and must understand and address the needs and aspirations of the people they serve.
The Code of Professional Ethics should be treated like an oath, which guides teachers to pursue truth, excellence, self-direction and self-discipline. The conduct of teachers must follow the principles of five key areas of professional activity:
1- Relationship of teachers with students
Teachers should respect the fundamental right of every child to education and recognize his/her potential and talent. They have to create a nurturing and supportive learning environment.
2- Teachers’ relationship with their profession and colleagues
Teachers must maintain the dignity and prestige of the teaching profession. They should cooperate and support their colleagues, fostering a positive and collegial work environment.
3- Relationship of teachers with management/administration
Teachers must maintain professional and respectful relationships with school management and administration while adhering to policies and regulations.
4- Relationship of teachers with parents/guardians
Teachers should involve parents and guardians in the educational process, promoting open communication and collaboration for the betterment of students.
5- Relationship of teachers with society and nation
Teachers should recognize their role as contributors to the development of society and nation. They should be aware of their responsibilities in shaping responsible and conscious citizens.
By following these professional ethics, school teachers can contribute significantly to the growth and progress of their students and the wider community. Professionalism, ethical conduct and commitment to their roles as teachers ensure that the teaching profession is held in the highest regard.
BY: TEAM KALYAN INSTITUTE
You can also check out these posts of ours 👇👇👇
Raksha Bandhan (Rakhi) Festival
Digital Inclusion Among Rural Minority Women
